P2 lacks typical morphosyntactical parts of speech, such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs, although they do exist semantically.
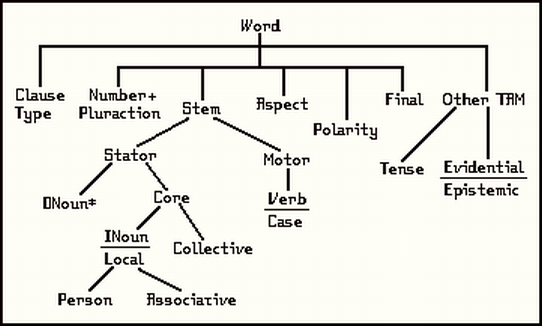
P2 has only two kinds of words: composites and particles. Particles are subdivided according to the syntactical function they perform. They aren't inflected, but may be proclitic. Each composite has a stem composed of two parts: a noun or pronoun part (stator) followed by a verb or case part (motor), cases and pronouns providing semantic linkage and noun roots and verb roots providing content. Composites are inflected for number, pluractionality, volition, and effect and may also be modified by additional roots.
Some noun roots are independent and denote sets of entities while others are dependent and denote functions (in the mathematical sense; they select subsets of the stem's referent, but usually not by simple intersection). A composite's basic noun root is always independent and any dependent noun roots precede it.
It should be mentioned that many dependent noun roots correspond to verb roots with similar meanings and that some of these are actually stems derived from the verb roots. However, they denote inherent characteristics, unlike the verb roots.
The morphology of a composite is show by the outline and graph below:

P2 quantifiers behave as verbs rather than as nouns.
| Key | Description | Glosses |
|---|---|---|
| -e, -E | = existential (indefinite) | "some", "any" |
| -z, -Z | = negative existential | "none" |
| -u, -U | = universal | "all", "every" |
| -v, -V | = negative universal |
The word components are grouped this way due to morphonotactic interaction. They will be grouped by semantics in the Syntax chapter.
Pronominal roots use the designations given in the following table; where two are given, the upper case is for kinds and the lower case for entities; this is paralleled in the forms column. The personal pronominals can be modified for association instead; the latter forms are in parentheses. The tag for kinds is -Kin and the tag for association is -Asc.
| Key | Forms | Description | Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| k- | ki (kya:) | k-person (singular) | personal |
| l- | li (lya:) | l-person (singular) | |
| m- | me (mya:) | = k + l (inclusive) | |
| o- | de (dya:) | anaphoric (obviative). | |
| p- | ci (ca:) | anaphoric (proximative). | |
| s-, S- | to, te: | preceding proposition | subordinating |
| t-, T- | za, ze: | following proposition | |
| r-, R- | go, ge: | restrictive relative | relative |
| n-, N- | no, ne: | indefinite relative | |
| q-, Q- | fi, fye: | interrogative (content question) | other |
| w-, W- | wa, we: | generic noun | |
| x- | xa | reflexive | coreference |
| y- | o | pivot (conjunctive) |
The 2nd column under Forms shows the case roots combined with the collective entity marker (-Col) and the 1st shows them without. A collective form can't be used with either the non-associative form of a personal pronominal, the reflexive, or the pivot.
| Forms | Tag | Role Name | Role Description | Finals | Implied | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ny, ni | nni | Don | Donor | entity providing theme | all | Vol | Una |
| ty | nty | Agt | Agent | entity performing action | all | Vol | Una |
| r, ro | mro | Beh | Beholder | entity perceiving situation | all | Inv | Una |
| k | nk | Sub | Subject ? | entity located | all | Inv | Una |
| k | nk | Def | Defined ? | entity identified or defined | none | - | |
| vo, va | nva | Rcp | Recipient | entity receiving theme | -IU, -VU | Inv | - |
| pi | mpi, mpye | Pat | Patient | entity undergoing process | -IU, -IA | - | Aff |
| Tag | Description | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| -S | 1 entity | 1 occasion | |
| -P | 2+ entities | 1 occasion | |
| -HabS | 1 entity | 2+ occasion | |
| -Dia | 2+ entities | 2+ occasion | but 1 entity per occasion and vice versa |
| -HabP | 2+ entities | 2+ occasion | unlimited combination |
| Tag | ??? | ??? | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| -IU | Inv | Una | unmarked |
| -IA | Inv | Aff | |
| -VU | Vol | Una | |
| -VA | Vol | Aff |
| Tag | Description | Glosses |
|---|---|---|
| Now- | absolute present | "now" |
| Pst- | definite past | "then" |
Sentence-type and clause type marking are accomplished using proclitic particles. These are:
| Key | Forms | Description | Glosses | Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | po= | declarative (statements) | sentence-type particle | |
| ! | sa= | imperative (commands) | ||
| ? | je= | interogative (polar questions) | ||
| & | do= | logical conjunction | "and" | conjunctive clause-type |
| | | bi= | logical disjunction | "and/or" | |
| # | he= | logical exclusion | "or" | |
page started: 2010.Jun.17 Thu
current date: 2010.Jun.26 Sat
content and form originated by qiihoskeh
Table of Contents